Disclaimer: Opinions expressed by the author do not necessarily reflect those of the veterinary reviewer.
It is always a worrisome moment when we notice something wrong with our pets. We don’t like to think of our beloved feline friends being injured, hurt, or feeling unwell, especially as they can’t speak to us to inform us what may have happened or how they are feeling. Nor can they understand our offering of reassuring words to them in the same way a child or partner can.
If your cat has started limping yet they are still jumping and running around, you may be wondering what could be wrong with them. In fact, you might think nothing is really wrong at all since they are still darting around.
This is where different communication and understanding needs to come in. Your cat can’t tell you what is wrong, but limping is a sure sign that they need to get checked out by a vet, even if they are still running and jumping. Let’s look at some of the potential causes.
Why Is My Cat Limping but Not Showing Signs of Pain?
While cats are predatory animals and can often be considered to be quite ruthless creatures, they happily and fearlessly hunt mice, birds, and other small prey. However, despite this, they are also prey animals. Perhaps because of the danger of being another animal’s target, an instinct not to show or display pain (injury and illness) remains in cats, even though they are domesticated and not wild.
Cats won’t express pain unless vital or the pain or illness has reached a point where they no longer have the option but to demonstrate their pain or vulnerability.
While there are many reasons for their limping, which we will look at next, do not assume your cat is not in pain or feeling stressed just because they are still jumping, running, etc. In general, your cat is shifting their weight because something is sore. Alternatively, there could be a nerve problem. There are subtle signs of pain you can watch out for, but any limp should be cause for concern.

Causes of Cat Limping
Cats do not limp for no reason, so if you see that they are lame either on their front leg or back leg, it needs investigating. The severity can range from a mild limp to non-weight bearing. Commonly, it is just one limb, but not always. There are a multitude of causes behind the limping, and this will need to be looked at and diagnosed by your veterinarian.
Some of the most common causes of limping in cats include:
- Fracture or dislocation
- Sprain or strain
- A foreign body, such as a thorn, stuck in the paw or paw pad
- Broken or torn nail
- Ingrown nail
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Arthritis
- Tumor (anywhere on the affected limb, not just the paw)
- Cat bite or abscess
- Ligament or tendon injury
- Bruising
- Wound (cuts, lacerations, or grazes)
- Burns (heat, cold, or chemical)
Signs Your Cat Is in Pain
As discussed, your cat will show more subtle signs of pain than obvious ones. These signs may become more apparent as the pain continues or increases, but learning how to read felines is a major benefit to their health. It means you can act quicker and your kitty receives help sooner instead of the problem worsening and their well-being declining.
- Limping itself is a sign of pain and not the actual problem or cause
- Reduced eating or not eating
- Sleeping more/ less activity
- Sleeping in a different area than normal
- Behavioral changes
- Aggression
- Retreating or hiding
- Being more vocal or louder
- Not happy when you touch or stroke them
- Pull the affected limb away from you if you try to touch or examine it
- Licking painful area

Should I Go to the Vet?
Limping or any other sign of pain and discomfort is always worth a trip to your veterinarian or at least a phone call, especially if you can also see other signs of discomfort or if the lameness has continued for more than 12–24 hours. It’s better to err on the side of caution. While you are waiting for your consultation, keep your cat rested.
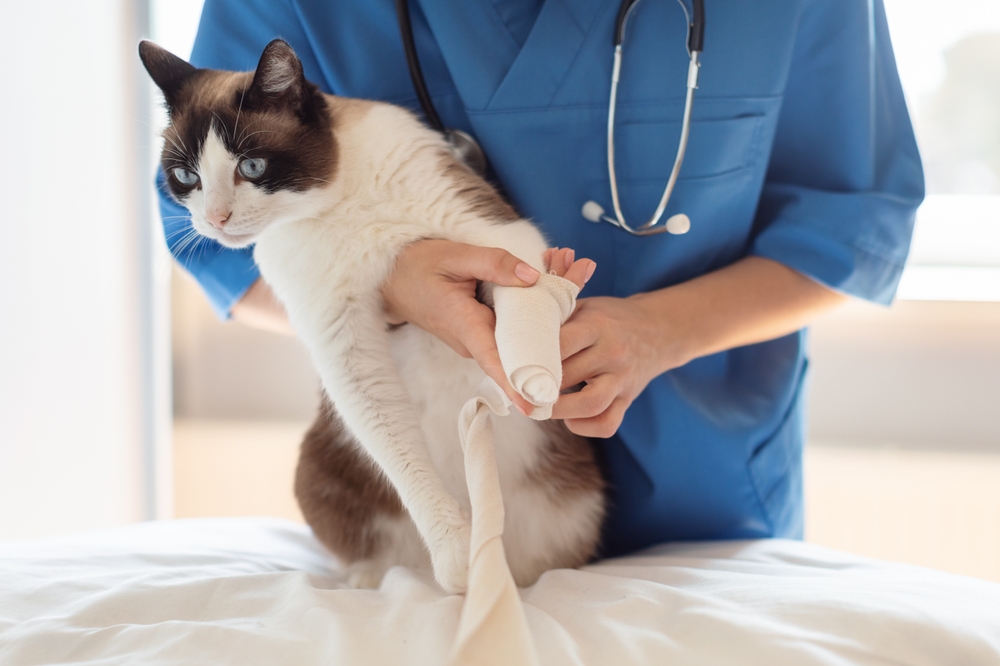
Treatment for a Limping Cat
To diagnose the cause of your cat’s limp, your vet will have to investigate the issue further. This can and likely will take a variety of routes and will be different for each cat. There are various examination tools and treatments available, but the ones your cat will receive will be dependent on the findings and the cause found.
Here are a few common examples of investigations and treatments your vet may prescribe. They may use one of these, all of them, or order extra tests and treatments not mentioned here.
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
- X-Rays
- Ultrasound scans or MRI
- Further and more detailed examination under sedation or anesthesia
- Surgery
- Wound flushing and care
- Bandage or dressing support
- Medication (oral or injectable), such as antibiotics and painkillers


Conclusion
Cats are complex and mysterious animals, and we love them for it. However, limping is a sure sign of pain and that something is wrong, even if they can still run around and jump onto the couch.
The instinct not to appear vulnerable is as strong today in domesticated cats as it was with their wild ancestors and fellow big cat friends. Do not ignore a limp thinking they are okay just because they are moving a lot. Instead, have them checked over by a vet to prevent the situation from worsening and so that your cat can receive the correct treatment rather than be uncomfortable longer than necessary.
Related Reads:
- My Cat Is Limping & Not Eating, What Do I Do?
- My Cat Has a Front Paw Limp, What’s Wrong? Vet Approved Advice
Featured Image Credit: Amada Ekeli, Shutterstock












