Click to Skip Ahead
Your feline friend’s round belly is often cute and endearing. While that roundness is typically the result of too many treats (which isn’t great in itself), it can also be the result of ascites, or fluid accumulation in the abdomen. Ascites is a sign of disease and often a serious one. So, if you notice that your cat’s belly is suddenly fuller, rounder, or tighter, especially if you’re seeing other signs, contact your veterinarian immediately.
What Is Ascites in Cats?
Every abdomen, feline or otherwise, has a small amount of fluid in it, which helps cushion the organs and maintain business as usual. The amount is kept in check by regular balances in the blood and surrounding tissue. Ascites is the name for when that fluid level exceeds normal limits. The amount of fluid accumulation can be small, only noticeable on imaging, or large, and anyone who saw your cat would notice that something’s wrong.
Ascites isn’t a disease in itself; rather, it’s a sign of many different types of diseases. The fluid that accumulates can be made up of blood, serum, or even urine. It can be incredibly uncomfortable, especially in high amounts, as that extra fluid adds pressure to abdominal organs—most notably, the digestive system—and the diaphragm, sometimes making it hard for a kitty to breathe.
What Are the Signs of Ascites in Cats?
Ascites is a sign in and of itself, but it also has signs of its own. These will differ depending on what’s causing the fluid accumulation and how much fluid is in there. So, cats with ascites may present any of the following:
- Abdominal swelling
- Discomfort, especially when lying down
- Lethargy
- Decreased appetite
- Nausea, vomiting
- Difficulty or labored breathing
- Coughing
Depending on the cause, you may also see:
- Pale gums
- Lack of urine
- Tires quickly or exercise intolerance
- Fever
- Increased drinking/urinating
What Are the Causes of Ascites in Cats?
A cat’s abdomen doesn’t just randomly decide to start hoarding fluid. But what causes fluid buildup in a cats stomach? Instead, ascites is brought on by many different causes, affecting anything from the blood vessels to the bladder.
- Trauma: Falls or being hit by a car are common causes of internal bleeding or rupture of the urinary bladder, which can lead to ascites.
- Heart failure: When the right side of the heart is struggling, it often can’t pump the necessary amount of blood into the lungs, so that blood backs up into the body, enabling fluid to escape into the abdomen.
- Loss of protein in the blood: Proteins like albumin are needed in the blood to retain fluid in the bloodstream. If those proteins are lost through kidney issues or parasites or not made at all due to liver disease, fluid can escape the bloodstream and congregate in the abdomen.
- Bladder rupture: Trauma isn’t the only thing that can cause the urinary bladder to rupture; urethral blockage from a stone or blood clot can also do it, causing urine to flood the abdomen.
- Infection: Infections in the abdomen or its lining (called the peritoneum) can lead to inflammation and the release of fluid from the surrounding tissue. The most famous culprit of this is feline infectious peritonitis.
- Cancer: Any tumor type or size in the abdomen can lead to ascites in a similar way that infections do, which is inflammation. Tumors may also bleed, making blood accumulate where it shouldn’t, and the tumor itself can contribute to a swollen abdomen if it takes up a large amount of space.
How Do I Care for a Cat With Ascites?
There is nothing that you can do at home for a cat with ascites; it’s a veterinarian-only situation. Keep in mind that small amounts of fluid accumulation can go unnoticed, especially to the naked eye, so your cat may have ascites and you won’t know it without proper imaging. Whether your cat’s belly appears enlarged or not, though, see your veterinarian if you notice any concerning signs.
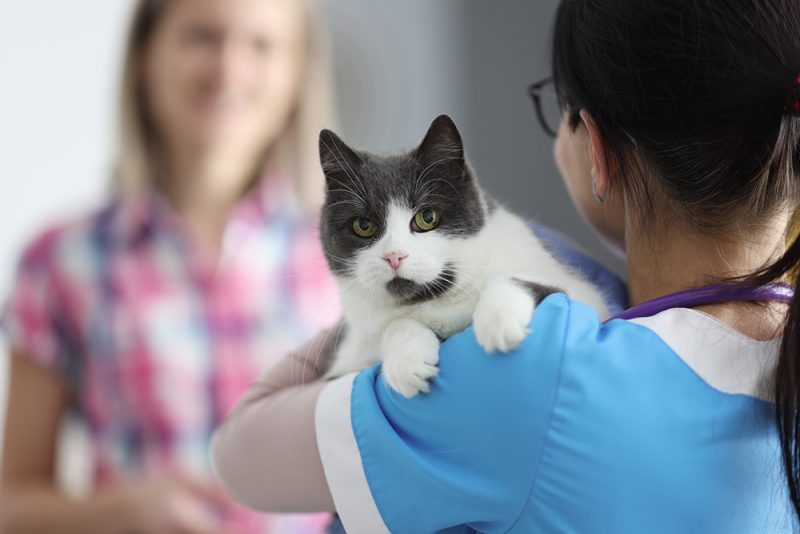
Veterinary Diagnosis With Ascites
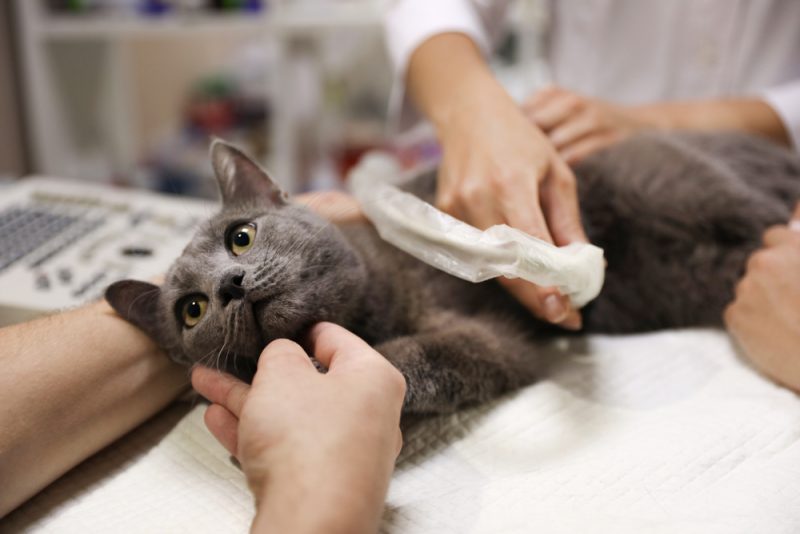
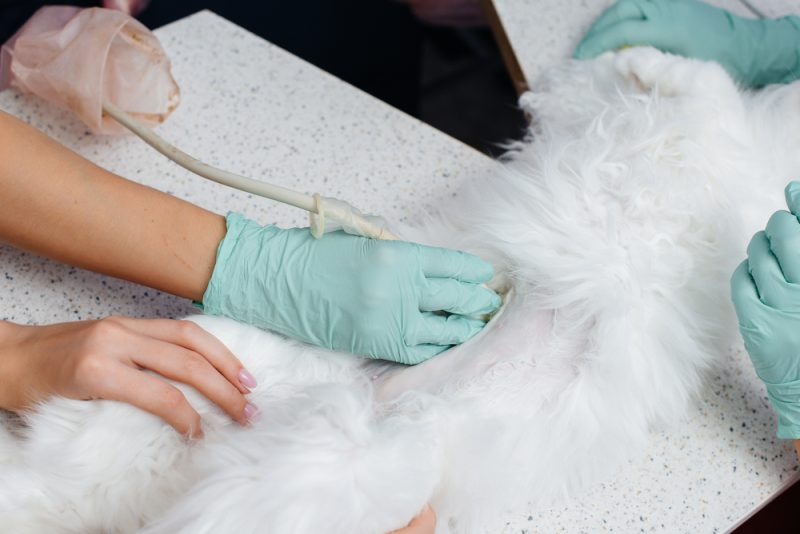
Your vet will first need to find out what is causing the abdominal enlargement. X-rays or ultrasound may be required to determine if it’s true ascites or something else. From there, there are many routes that your vet may take, mainly depending on other signs or findings.
They may investigate the heart if your kitty is also having difficulty exercising or if it doesn’t sound quite right when they listen to their chest through a stethoscope. They may run blood work or do a urinalysis to check protein levels and organ function and see what the urine’s up to. Also, they may try to grab a bit of the abdominal fluid using a syringe, needle, and ultrasound guidance. Analyzing the fluid will tell them what it’s made up of so they can further look into things like infection, cancer, etc.
Veterinary Treatment of Ascites
The main way of reducing fluid accumulation in the abdomen is to correct the cause of it getting there in the first place. That may include antibiotics, heart medications, diuretics, surgery, chemotherapy, or supportive care. Sometimes the cause can’t be fixed, so a vet may decide to periodically drain the fluid in order to make the kitty more comfortable.
The cause and treatment for the underlying sources of ascites are best handled in the early phases, so be sure to see your vet any time you notice that something is off with your kitty, especially if they have an enlarged abdomen.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How Long Do Cats Live With Ascites?
Since ascites in cats has many possible causes, so does the amount of time that a cat can live with it. Generally, though, ascites is a sign of various significant diseases that may require lifelong treatment, are costly to treat, or have no treatment.
Does Ascites Mean End-Stage?
Developing ascites isn’t a good thing. It’s usually the result of a major health malfunction, such as cancer or heart failure. Catching the issues early can help your cat get proper treatment so they can have a longer and higher-quality life, but many of the health issues that lead to ascites are quite serious.
What Happens If Ascites Isn’t Drained?
The first approach to getting rid of ascites is to treat the underlying condition. Once it’s properly managed, the fluid will often decrease on its own. In cases where a vet chooses to drain the fluid, they do so to make a kitty more comfortable. The more fluid that accumulates, the more discomfort the cat can feel. It can create enough pressure that it’s difficult to breathe, eat, or lie down.

Conclusion
Fluid accumulation, or ascites in cats, is not a normal thing for your pet to experience. It can be a sign of various serious issues, including cancer, heart failure, or an infection. If you notice a change in the size, shape, or firmness of your cat’s belly, especially if they are showing other signs of not eating, difficulty breathing, or lethargy, see your vet immediately.
Featured Image Credit: Libre, Shutterstock











